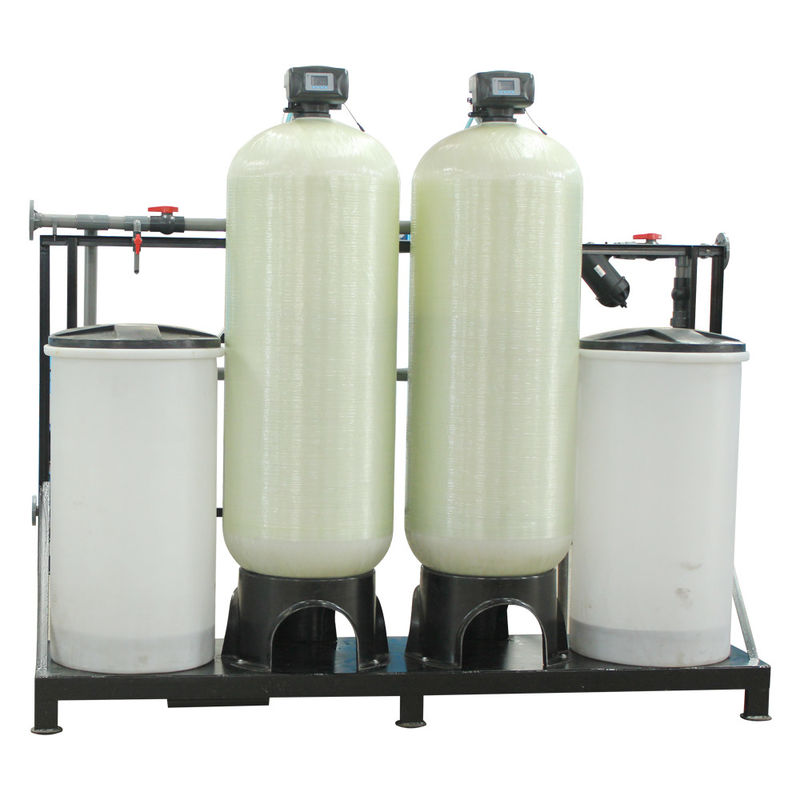
Commercial Ion Exchange Water Purification System
Product Details:
| Place of Origin: | China |
| Brand Name: | Fenigal/OEM |
| Certification: | CE/NSF etc. |
| Model Number: | WS-X-CW |
Payment & Shipping Terms:
| Minimum Order Quantity: | 1 Set |
|---|---|
| Price: | Negotiable |
| Packaging Details: | Standard Export Wood Crate/Carton or Naked wrapped by film/Containerized |
| Delivery Time: | 15~30 days |
| Payment Terms: | T/T, Western Union, Paypal etc. |
| Supply Ability: | 200 set per month |
|
Detail Information |
|||
| Technology: | Ion Exchange | Material: | FRP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design: | Skid Mount/containerized | Water Temp.: | 5~35˚C |
| Water Flow Rate: | Up To 10m3/h.vessel | Voltage: | 380V,415V,220V,can Be Customized |
| Application: | Surface, Underground Water, Sewage Water Treatment | Size: | Dia.50cm~200cm |
| Highlight: | FRP 380V Ion Exchange Water Purification System,380V Ion Exchange Water Purification System,FRP commercial water softener system |
||
Product Description
Commercial ion exchange deionizer Softener price purification treatment for cooling water
Water pressure:0.18-0.6Mpa Working temperature:1°c-55°c
Hardness of raw water: <8mmol/L Operation method:manual/automatic
Hardness of effluent water: ≤0.03mmol/L water flow: 0.3-20 t/h
Rebirth method:
Control method: time or flow
Working electric: 220V/50Hz
Hard water is water with a high dissolved mineral content, while soft water has a relatively low concentrated of dissolved minerals. All water, except for water that has been meticulously distilled, will have some dissolved minerals, since water is an excellent solvent and it readily combines with the substances it comes into contact with. High concentrations of minerals can be problematic, however. Hard water is not generally harmful, but it can be irritating and will shorten the life of home appliances like dishwashers and washing machines.
The most common minerals dissolved in household water are calcium and magnesium, although other minerals may certainly be present as well. These substances can cause serious problems for home appliances when they precipitate out, forming a characteristic scale that may accumulate in pipes and around faucets. If the scale is not promptly removed, it can start to clog pipes and can damage things like water heaters and dishwashers, which cannot cope with the minerals.
Most people notice problems with hard water not because of the scale formation, but because it interferes with the action of soap. Soaps and detergents lather poorly in waterthat contains minerals, and as a result people tend to use more, causing thick scum to form. In addition, it's hard to get clean properly when washing with hard water, and some people feel constantly slightly dirty when they wash with it. It also leaves residue in hair that can make hair hard to manage.
The softener resin tank contains the treated ion exchange resin - small beads of polystyrene. The resin beads initially adsorb sodium ions during regeneration. The resin has a greater affinity for multi-valent ions such as calcium and magnesium than it does for sodium. Thus, when the hard water containing the Calcium and Magnesium Ions is passed through the resin bed, the calcium and magnesium ions adhere to the resin, releasing the sodium ions until equilibrium is reached. The water softener has exchanged its sodium ions for the calcium and magnesium ions in the water.
Regeneration is achieved by passing a NaCl solution through the resin, exchanging the hardness ions for sodium ions. The resin’s affinity for the hardness ions is overcome by using a highly concentrated solution of brine. The regeneration process can be repeated indefinitely without damaging the resin.
Technical parameter
|
1. Treatment effect:
①. Iron content: ≤0.3mg/L;
②. Manganese content: ≤0.1mg/L;
③. Turbidity of effluent: <3FTU.
|
|
2. Water inlet requirements:
①. Iron content: ≤20mg/L;
②. Manganese content: ≤3mg/L;
③. Influent turbidity: <20FTU;
④. Alkalinity: ≤2mg/L;
⑤. pH value:> 6.0 (when removing iron),> 7.5 (when removing manganese).
|
|
3. Working environment parameters
①. Working temperature: 5-60℃ (special temperature can be customized);
②. Working pressure: ≤0.6MPa.
|
|
4. Operating parameters
①. Working method: pressure type;
②. Operation mode: water flow from top to bottom, series (high iron and manganese content) or parallel;
③. Filtration speed: 6-10m/h (when removing iron), 5-8m/h (when removing manganese);
④. Operating cycle: depending on the quality of the raw water, the minimum is not less than 8 hours;
⑤. Backwashing method: water washing, or air-water combined backwashing;
⑥. Backwash time: 10-15min;
⑦. Water consumption for backwashing: 1-3%;
⑧. Backwash intensity: 15-20L/s·m2.
|
How does water softener work?(Principles of Ion Exchange to Soften Water )
Calcium and magnesium ions are atoms having a positive electrical charge, as do sodium and potassium ions. Ions of the same charge can be exchanged. In the ion exchange process, a granular substance (usually a resin) that is coated with sodium or potassium ions comes into contact with water containing calcium and magnesium ions. Two positively charged sodium or potassium ions are exchanged (released into the water) for every calcium or magnesium ion that is held by the resin. This “exchange or trade” happens because sodium or potassium are loosely held by the resin. In this way, calcium and magnesium ions responsible for hardness are removed from the water, held by the resin, and replaced by sodium or potassium ions in the water. This process makes water “soft.” Eventually, a point is reached when very few sodium or potassium ions remain on the resin, thus no more calcium or magnesium ions can be removed from the incoming water. The resin at this point is said to be “exhausted” or “spent,” and must be “recharged” or “regenerated.”
The principle of sodium ion exchange and softening treatment is to exchange cation in the raw water with resin, hardness constituents Ca2+and Mg2+ in water exchange Na+ in resin, thus absorb the Ca2+and Mg2+ to make the water to be softened.
2RNa + Ca2+ = R2Ca + 2Na+
2RNa + Mg2+ = R2Mg + 2Na+
After the water treated by sodium ion exchanger, the Ca+ and Mg+ were superseded by Na +.
The Brine Tank
The brine tank is just what its name suggests, a plastic tank that contains a brine, water saturated with salt. The brine solution is typically made with salt or sodium. However problems may result if you are on a restricted low sodium diet in that some of the sodium is transmitted into the drinking water.
Also, the bacteria in septic systems so necessary for the breakdown of waste may be adversely affected by high concentrations of sodium.
The Control Valve and Regeneration
The control valve is the traffic cop in your water softener system. It determines when it is time to clean those plastic beads which are now coated with calcium and magnesium. Older style units use a timer, newer models use a computer controlled meter that determines when it is time based on actual water usage.
To clean the beads the water softener uses a process often called regeneration which consists of three cycles: Backwash, Recharge and Rinse.
Backwash:
Regeneration starts with a backwash cycle where the valve reverses water flow in the tank and flushes the tank of debris. The debris is then eliminated out the drain.
Recharge or Regeneration:
In the Recharge cycle the salty brine solution is pumped into the mineral tank. The highly concentrated salt solution with its positive electrical charge is attracted to the negatively charged plastic beads and forces the magnesium and calcium off the beads.
The salt or potassium by itself is not positively charged enough to displace the magnesium or calcium in normal concentrations, but in the highly concentrated solution of brine, it is strong enough to force the calcium and magnesium off.
The excess magnesium and calcium rich salty water is then flushed out of the tank and down the drain.
Rinse:
The tank is then filled and rinsed with water and the process repeats itself. The beads are now coated with salt. As the calcium and magnesium from the hard water are attracted to the plastic beads, the salt, now in much diluted quantities and smaller electrical charge, is forced off the beads and is suspended in the softened water.
When the beads become nearly all coated with minerals, the control valve starts a new regeneration cycle and cleans them again, flushing the hard water minerals down the drain.
Application scope of softener
Mainly used in industry and civil water softening preparation, such as Boiler feed water make-up water, air conditioning system make up water, heat exchanger, power plant, chemical, textile, printing and dyeing, bio-pharmaceutical, Electronic system and water pretreatment.
![]()
![]()
![]()